Enzymes are proteins or RNAs produced by living cells
that are highly specific and catalytically efficient for their substrates. Biocatalysis
is a technology that uses enzymes as catalysts to facilitate synthetic
reactions and has many advantages over traditional chemical synthesis. Biocatalysis
technology avoids the use of toxic catalysts and, due to the mild reaction
conditions, water is used as a solvent so generating less waste and toxic
by-products. Meanwhile, Biocatalysis technology possesses a high degree of
specificity, which can effectively shorten the synthetic route and provide better
stereoivity and catalytic efficiency.

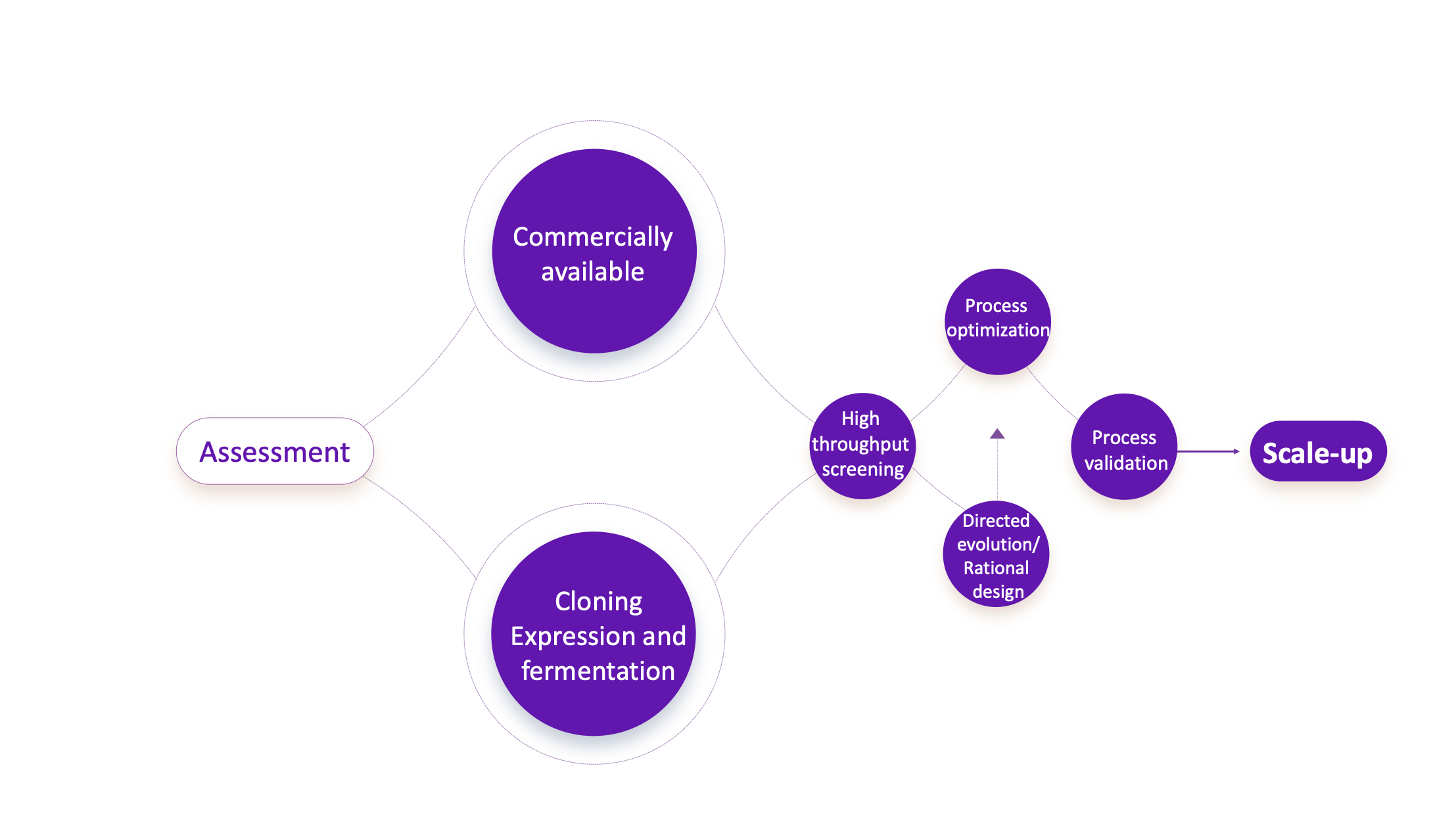
With years of research and technical know-how accumulation, we have mastered biocatalysis technology and built an enzyme catalytic chemistry platform. This platform integrates enzyme construction, enzyme fermentation, enzyme screening, enzymatic process optimization and scale-up manufacturing. The construction of an autonomous enzyme library refers to the introduction of target enzyme genes into host cells (usually E. coli or yeast cells) using molecular biology techniques, followed by the fermentation and optimized expression of recombinants containing the target genes to produce a large number of target proteins, i.e., enzyme proteins required for specific reactions.
We apply biocatalysis technology to reductase-catalyzed reactions, lipase-catalyzed reactions and transaminase-catalyzed reactions, and we have several cases of successful application of biocatalysis technology for scale-up manufacturing.
For some specific reactions, we choose target enzymes by high-throughput screening from existing enzyme libraries, and then perform process optimization in terms of relevant chirality and conversion rate to improve respective parameters for chiral swift synthesis and chiral separation based on the preliminary screening results and product target requirement.